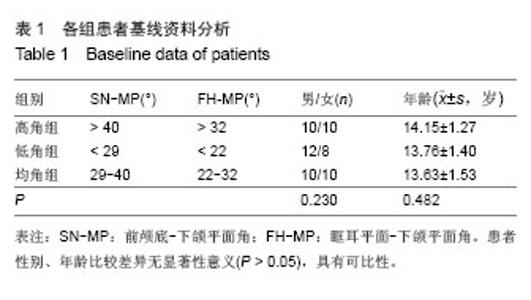
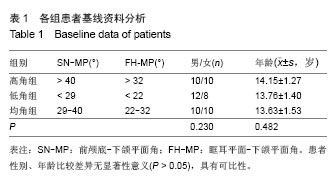
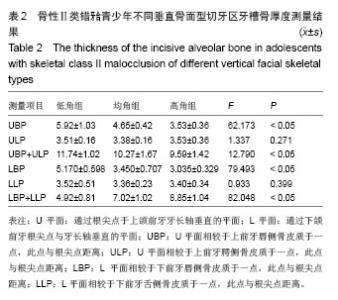
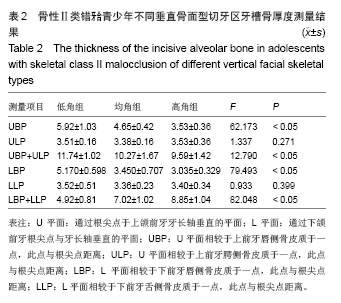
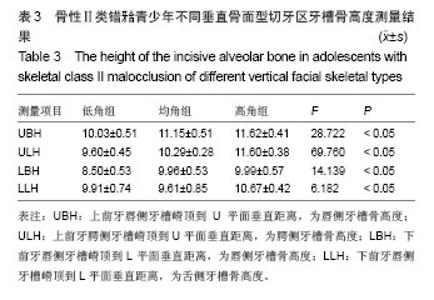
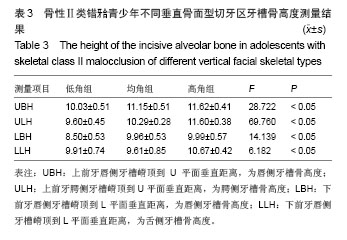
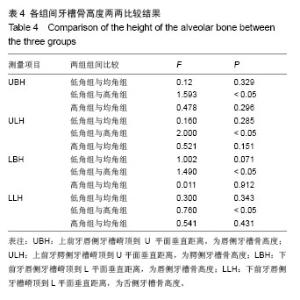
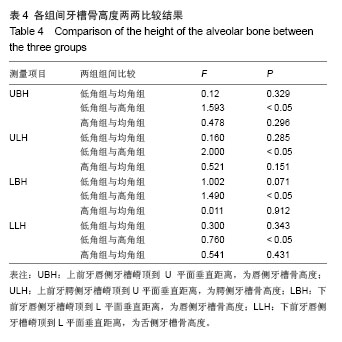
| [1]傅民魁,张丁,王邦康,等.中国25392名儿童与青少年错合畸形患病率的研究[J].华口腔医学杂志,2002,37(5):371-373.
[2]王胜林,戴红卫.骨性Ⅱ类错合颅面形态特征研究进展[J].人民军医,2006,49(11):669-670.
[3]Verma SL,Sharma VP,Sinqh GP,et al.Comparative assessment of soft-tissue changes in Class II Division 1 patients following extraction and non-extraction treatment. Dent Res J(Isfahan).2013;10(6):764-771.
[4]田野,叶禹,白丁.骨性Ⅱ类畸形拔牙掩饰治疗策略[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2010,3(5):261-265.
[5]梁妍华,栗震亚.兰州地区汉族青少年软组织侧貌唇位的评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(20):3777-3784.
[6]Baysal A,Ucar F,Buyuk SK,et al.Alveolar bone thickness and lower incisor position in skeletal Class I and Class II malocclusions assessed with cone-beam computed tomography. Korean J Orthod.2013;43(3):134-140.
[7]Gracco A,Lombardo L,Mancuso G,et al.Upper incisor position and bony support in untreated patients as seen on CBCT. Angle Orthod.2009;79(4):692-702.
[8]Enhos S,Uysal T,Yagci A,et al.Dehiscence and fenestration in patients with different vertical growth patterns assessed with cone-beam computed tomography.Angle Orthod.2012;82(5): 868-874.
[9]Hua Y,Nackaerts O,Duyck J,et al.Bone quality assessment based on cone beam computed tomography imaging.Clin Oral Implants Res.2009;20(8):767-771.
[10]Makedonas D,Lund H,Hansen K.Root resorption diagnosed with cone beam computed tomography after 6 months and at the end of orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances.Angle Orthod.2013,83(3):389-393.
[11]Uysal T,Yagci A,Ozer T,et al.Mandibular anterior bony support and incisor crowding: Is there a relationship?.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2012;142(5):645-653.
[12]Ahn HW, Lee DY, Park YG, et al.Accelerated decompensation of mandibular incisors in surgical skeletal class III patients by using augmented corticotomy: a preliminary study.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2012;142(2):199-206.
[13]Alexxander RG.亚历山大直丝弓技术一口腔正畸矫治原理与实践[M].邵金陵,冯雪.等译.西安:世界图书出版西安公司, 2001: 67-68.
[14]Ahn Hw,Moon SC,Baek sH.Morphometric evaluation of changes in the alveolar bone and roots of the maxillary anterior teeth before and after en masse retraction using cone-beam computed tomography.AngleOrthod.2013;83(2): 212-221.
[15]Grib DG,Yatabe Ms,OzawaTO,et aL.Alveolar bone morphology under the Perspective of the computed tomography: defining the biological limits of tooth movement. Dental Press J Orthod.2010;15(5):192-205.
[16]Bruno AG, Broe KE,Zhang X,et al.Vertebral size, bone density, and strength in men and women matched for age and areal spine BMD.J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(3):562-569.
[17]Fuhrmann RAW.Three-dimensional evaluation of periodontal remodeling during orthodontic treatment.Semin Orthod. 2002; 8(1):23-28.
[18]Shoreibah EA,Ibrahim SA,Attia MS,et aL.Clinical and radiographic evaluation of bone grafting in corticoto my facilitated orthodontics in adults.J Int Acad Periodontol. 2012; 14(4):105-113.
[19]Yagci A,Veli I,Uysal T,et al.Dehiscence and fenestration in skeletal C1ass I, Ⅱ and Ⅲ malocclusions assessed with cone-beam computed tomography.Angle Orthod. 2012;82(1): 67-74.
[20]Kook YA,Kim G,Kim Y.Comparison of alveolar bone loss around incisors in normal occlusion samples and surgical skeletal class IIIpatients.Angle Orthod.2012;82(4):645-652.
[21]Patcas R, Müller L, Ullrich O, et al. Accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography at different resolutions assessed on the bony covering of the mandibular anterior teeth.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;141(1):41-50.
[22]YamadaC,Kitai N,Kakimotoe N,et al.Spatial relationships between the mandibular centra l Incisor and associated alveolar bone in adults with mandibular prognathism.Angle Orthod.2007;77(5):766-772.
[23]Yu Q,Pan XG,Ji GP, et al.The association between lower incisal inclination and Morphology of the supporting alveolar bone:a cone-beam CT study.Int J Oral Sci.2009;1(4):217-223.
[24]张莉,王博,房兵.骨性Ⅲ类错下前牙区牙槽骨形态的锥形束CT分析[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,1(10):38-41.
[25]钟金晟,柳登高,欧阳翔英,等.应用锥形束CT评价前牙唇舌侧牙槽骨高度及厚度的研究[J].山东医药,2012,52(4):41-44.
[26]涂伶俐.正畸过程中的牙根吸收及其生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(7):1303-1306.
[27]Anwar N,Fida M.Evaluation of dentoalvcelar compensation in skeIetaI class II maIoccIusion in a Pakistani University HospitaI setting.Coll Physicians Surg Pak.2009;19(1):11-16.
[28]刘爱青,张继东.II类骨面型前牙深覆盖患者牙与牙槽骨特征分析[J].广东牙病防治,2011,19(12):627-630.
[29]陈晶晶,张端强.正常合青少年不同垂直骨面型切牙区牙槽骨宽度研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,4(4):232-234.
[30]叶艳艳,丁寅,李娟等.成人骨性II类错合患者不同垂直骨面型的切牙代偿情况研究[J].中国美容医学,2013,1(1):181-184.
[31]Nabila Anwar,Mubassar Fida.Compensation for vertical dysplasia and its clinical application. Eur J Orhod.2009; 13(1):1-7.
[32]Fontana M, Cozzani M,Caprioglio A.Soft tissue, skeletal and dentoal- veolar changes following conventional anchorage molar distalization therapy in class II non-growing subjects: a multicentric retrospective study.Prog Orthod.2012;13(1):30-41.
[33]Sarikaya S,Haydar B, Ciger S,et al.Changes in alveolar bone thickness due to retraction of anterior teeth. Am J Orthod Dentfacial.2002, 122(1):15.
[34]周蕾,周力,吴浩,等.不同面部生长型正常合及安氏II类1分类错牙合的前牙倾斜度及牙代偿特征[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2010, 28(5): 492-494.
[35]刘东旭,刘文.正常合中不同垂直骨面型切牙唇舌向倾斜度的测量分析[J].口腔正畸学,2003,10(4):175-177. |